查找算法之线性搜索算法实现
什么是查找算法
搜索算法用于检查元素或从存储元素的任何数据结构中检索元素。根据搜索操作的类型,这些算法一般分为两类
顺序搜索:在这种情况下,列表或数组将按顺序遍历,并检查每个元素。
线性搜索是最简单的搜索方法。
在线性搜索技术的搜索;在列表中按顺序搜索元素。
此方法可以在已排序或未排序的列表(通常是数组)上执行。
如果排序列表搜索从第0个元素开始,一直到从列表中找到该元素或该元素的值大于(假设列表按升序排序),则到达所搜索的值。
与此相反,在无序列表的情况下,搜索也从第0个元素开始,一直到该元素为止
线性搜索算法依次搜索数组中的所有元素。
它的最佳执行时间是1,而最差执行时间是n,其中n是搜索数组中条目的总数。
它是数据结构中最简单的搜索算法,检查元素集中的每一项,直到匹配搜索元素,直到数据收集结束。
当数据未排序时,首选线性搜索算法。
线性搜索被定义为一种顺序搜索算法,它从一端开始,遍历列表中的每个元素,直到找到所需的元素,否则继续搜索直到数据集的末尾。这是最简单的搜索算法
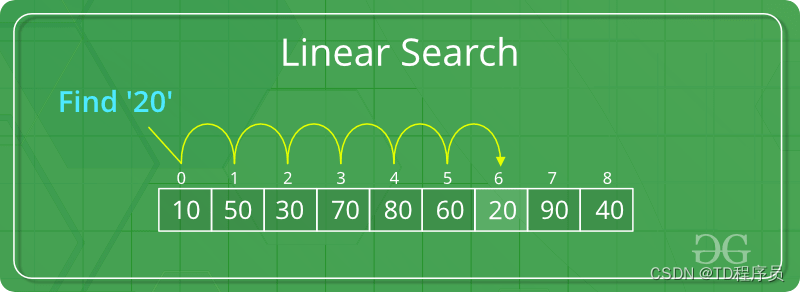
下图为线性搜索在给定的数字列表中找到元素“20”
线性搜索算法步骤
第一步:读取数组中的搜索元素。
第二步:在第二步中将搜索元素与数组中的第一个元素进行比较。
第三步:如果两者都匹配,显示“目标元素已找到”,并终止线性搜索功能。
步骤4:如果两者都不匹配,则将搜索元素与数组中的下一个元素进行比较。
步骤5:在此步骤中,重复步骤3和步骤4,直到搜索的元素与数组的最后一个元素进行比较。
第6步-如果列表中的最后一个元素不匹配,搜索失败
下面讲解一个例子,给定一个包含N个元素的数组arr[],任务是编写一个函数来搜索arr[]中的给定元素x。
按照以下思路来解决问题:
从0到N-1迭代,如果每个索引与return index匹配,则将每个索引的值与x进行比较
按照下面的步骤来解决问题:
将数组的第一个元素设置为当前元素。
如果当前元素是目标元素,则返回其索引。
如果当前元素不是目标元素,并且数组中有更多元素,则将当前元素设置为下一个元素,并重复步骤2。
如果当前元素不是目标元素,并且数组中没有其他元素,则返回-1,表示未找到该元素。
C实现方式
下面是上述方法的实现:
// C code to linearly search x in arr[]. If x
// is present then return its location, otherwise
// return -1#include int search(int arr[], int N, int x)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < N; i++)if (arr[i] == x)return i;return -1;
}// Driver's code
int main(void)
{int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };int x = 10;int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);// Function callint result = search(arr, N, x);(result == -1)? printf("Element is not present in array"): printf("Element is present at index %d", result);return 0;
}
输出结果:Element is present at index 3
C++实现方式
这里我们有一个向量,我们使用C++中的vector库的查找函数,即vector迭代器。
#include //Including the bits/stdc++ library for using vector and find functions
#include
using namespace std;int main()
{vector v{5, 15, 6, 9, 4}; // Declaring a vector v with initial valuesint key= 4; // Variable to store the element to be searchedvector::iterator it; // Declaring an iterator to// iterate through the vectorit = find(v.begin(), v.end(),key); // find function to search for the// element in the vectorif (it != v.end()) { // Checking if the element is// present in the vectorcout << key << " is Present in the vector"<< endl; // Printing if the element is present// in the vector}else {cout << key << " is Not-Present in the vector"<< endl; // Printing if the element is not// present in the vector}return 0;
}
输出结果
4 is Present in the vector
java实现方式
这里我们有一个列表,我们使用java中ArrayList库的查找函数
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args){List v = new ArrayList<>();v.add(5);v.add(15);v.add(6);v.add(9);v.add(4);int key = 4;if (v.contains(key)) {System.out.println(key+ " is Present in the list");}else {System.out.println(key + " is Not-Present in the list");}}
}// This code is contributed by divyansh2212
线性搜索递归方法
按照下面的步骤来解决问题:
如果数组的大小为0,则返回-1,表示未找到该元素。这也可以作为递归调用的基本条件。
否则,检查数组中当前索引处的元素是否等于key,即arr[size - 1] == key
如果等于,则返回找到的键的索引。
下面是上述方法的实现:
// C++ Recursive Code For Linear Search
#include
using namespace std;int linearsearch(int arr[], int size, int key)
{if (size == 0) {return -1;}else if (arr[size - 1] == key) {// Return the index of found key.return size - 1;}else {int ans = linearsearch(arr, size - 1, key);return ans;}
}// Driver's Code
int main()
{int arr[5] = {5, 15, 6, 9, 4 };int key = 4;// Function callint ans = linearsearch(arr, 5, key);if (ans == -1) {cout << "The element " << key << " is not found."<< endl;}else {cout << "The element " << key << " is found at "<< ans << " index of the given array." << endl;}return 0;
}
// Code contributed by pragatikohli
